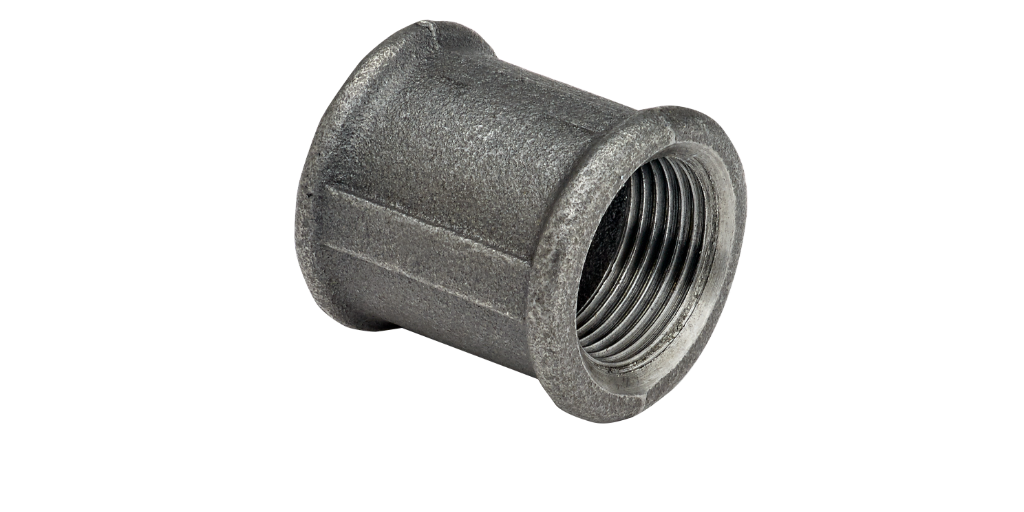
Threaded fittings are available as either male or female variants and rely upon the mechanical connection between the threaded tube and fitting to create a joint. The sealing efficiency and pressure integrity depends upon a number of factors: the mechanical seal created by the threads and associated deformation when they are tightened to a required torque; the type of thread profile (either parallel or taper) and whether a sealing compound, such as thread seal tape or a liquid or paste pipe sealant is used.
Threaded, or screwed and socketed joints, probably represent one of the oldest methods of joining gas or liquid pipework systems. They are typically used for smaller bore tubes. Threaded joints are demountable and reusable, and provide a heat free jointing method, suitable for used in pressure applications.
Different fitting materials are used for different applications - materials include malleable iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, duplex brass, dezincification resistant brass alloy (DZR) and gunmetal. There are various ways of defining the thread profiles and fitting sizes as a result of the decades of use. Threaded fittings and threaded profiles are therefore covered by a number of different standards, so it is important to ensure product compatibility.

 Carbon Steel Tubes
Carbon Steel Tubes